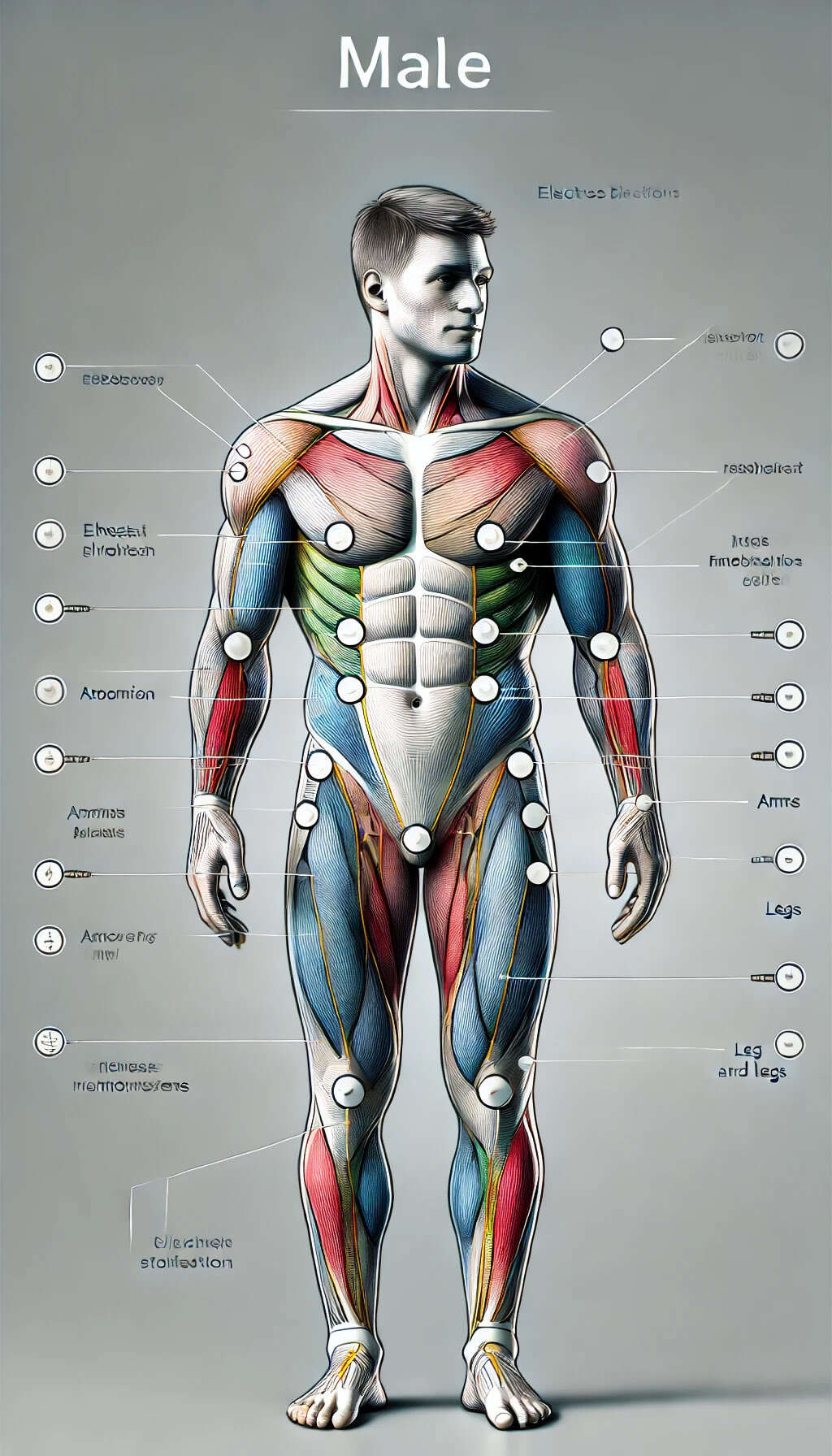
Male Electrode Placement for Electrical Stimulation: A Comprehensive Guide
Electrical stimulation is now well-known in multiple fields. Such as physiotherapy, sports medicine, and pain management. This method uses electrical stimulation by attaching electrodes to specific muscles, nerves, or tissues to help reduce pain, improve muscle functionality, and aid recovery.
Proper electrode placement is critical for optimal results. In this extensive guide, we will explain the electrical stimulation chart for male electrode placement and provide a complete guide on how to put it correctly to stimulate your body effectively.
What is Electrical Stimulation?
Electrical currents are used in electrical stimulation to stimulate nerves and muscles. Different forms of e-stim are transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (e.g., neuromuscular electrical stimulation) and (functional electronic stimulation).
There are types of TENS UNIT, and each type is used for a different purpose, like pain relief or muscle re-education.
If you are considering purchasing an electrode placement kit or a TENS unit, check out this product, which offers a variety of options for targeted electrical stimulation.
Understanding Male Anatomy
Before we discuss the placement of electrodes, it is about time to start with some knowledge of male anatomy. This will make it possible to determine which muscles and nerves must be treated.
Then you move on to arms (biceps, triceps, and forearms combined or not, depending on the person) and legs. A network of nerves controls involuntary or voluntary movement and sensation through the vitals.
Electrical stimulation selectively stimulates specific nerves in muscle groups, primarily for pain control.
Also Read: Pelvic Floor Male TENS Unit Pad Placement for ED
General Principles of Electrode Placement
- Make sure the skin surface is clean. Dirt and oils on the skin can block electrical currents from traveling through your body.
- Correct Gel Placement: A conductive gel is recommended to improve conduction and minimize skin irritation.
- Minimum Distances between electrodes: Set the distance of 1 inch clean to avoid overlapping electrical fields. If this field comes in contact it will generate very uncomfortable.
- Forced Placement: The electrodes used for the ECT should be placed so that they do not move during treatment, as movement will cause stimulation to become inconsistent.
Chart for Electrode Placement
| Condition | Electrode Placement Points | Tips for Placement |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Back Pain | Parallel to spine, above and below the pain area | Use cross-pattern with four electrodes |
| Knee Pain | Above and below patella, sides of knee | Avoid placing directly on the kneecap |
| Shoulder Pain | Anterior, posterior, and lateral deltoid | Adjust to avoid bony areas |
| Quadriceps | Upper thigh near hip, above knee | Ensure muscle is relaxed during placement |
| Hamstring | Upper hamstring near gluteal fold, above knee | Gradually adjust intensity to avoid cramping |
| Tennis Elbow | Lateral epicondyle, forearm muscles | Ensure firm placement to prevent movement |
| Calf Muscle Pain | Upper calf near knee, lower calf near ankle | Avoid placing on tendons |
Benefits Beyond Muscle Stimulation
Relieves Pain: Electrical stimulation is perfect for treating health conditions that result in chronic pain, like arthritis and fibromyalgia. Correct placement of electrodes to focus on the location(s) causing pain can reduce or eliminate symptoms.
Better Circulation: Stimulation can increase blood flow and reduce swelling in the treated area. This is especially good for injury recovery.
Faster recovery: Athletes frequently use electrostimulation to speed up recovery. It aids in combating muscle soreness and speeds recovery.
Read more: Where do You Put Tens Pads For Erectile Dysfunction?
Practical Tips for Effective E-Stim Use
- Regular Visits: Best results occur when the wears their e-stim as directed and prescribed by a physician.
- Use Better Intensities: Begin with lighter, then scale up as capable.
- Combine with Exercises: Pairing e-stim and active exercises can go a long way for the best results when it comes to muscle strengthening.
- Progress: Monitor your sessions and changes in pain or muscle strength levels over time to adjust the treatments depending on progress.
How to Use an Electrical Stimulation Chart?
An electrical stimulation chart is vital for clinicians and patients undergoing electrotherapy. To effectively use an electrical stimulation chart, follow these steps:
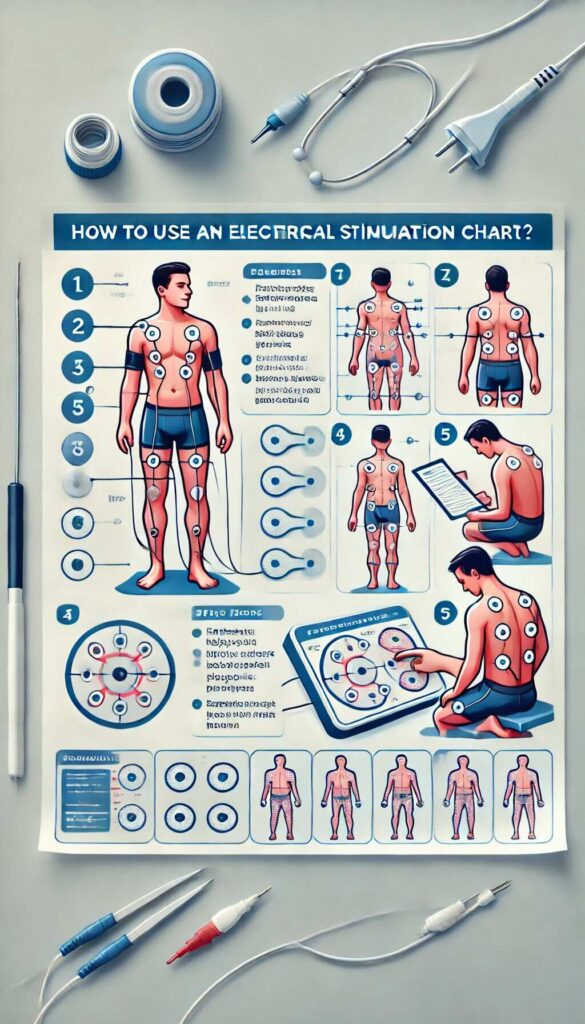
Familiarize With the Chart Layout
Get familiar with various elements of the chart, such as electrode arrangement diagrams, recommended frequency settings, number settings, and length and intensity.
Point the Target
First, locate where you have to aim, which means as a metabolism booster, and then hit. It may be in your muscles, swim, or other main organs. The chart will tell you where to host your electrodes for maximum results.
Frequency and Intensity Settings
Adjust the electrical stimulation device to the recommended frequency and intensity levels, as indicated on the chart. This is an important step because certain settings are appropriate for different conditions and treatment goals.
Respect the treatment time
Comply with the therapy time shown in the chart. Excessive stimulation can cause pain or muscle strain, so it is necessary to do the recommended time.
Track Response
Please monitor the body’s response while you are giving stimulation and afterward. Fine-tune if necessary and check the chart to ensure treatment is going in the right direction.
Electrode Placement for Muscle Strengthening
For muscle strengthening and rehabilitation, NMES is often used. Here are the standard placements:
Quadriceps:
- Place one electrode on the upper thigh, near the hip joint.
- Place the second electrode just above the knee cap.
- Strengthen the quadriceps muscle post-surgery or injury to improve knee stability.
Hamstrings:
- Position one electrode on the upper hamstring near the gluteal fold.
- Place the second electrode above the back of the knee.
- Strengthen hamstring muscles, aiding in knee stability and reducing the risk of injury.
Biceps:
- Place one electrode on the middle of the bicep muscle.
- Position the second electrode closer to the elbow.
- Enhance muscle strength and endurance in the bicep.
Calves:
- Place one electrode on the upper calf near the knee.
- Position the second electrode on the lower calf, just above the ankle.
- Strengthen the calf muscles, aiding in improved mobility and support.
Conclusion
Proper electrode placement is fundamental to the success of electrical stimulation therapy. Whether using TENS for pain relief or NMES for muscle strengthening, following these guidelines ensures safe and effective treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new therapy regimen to tailor the approach to your needs and conditions.
By understanding and implementing the correct techniques for electrode placement, individuals can maximize the benefits of electrical stimulation, leading to improved pain management, muscle strength, and overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Use Electrical Stimulation?
The frequency depends on your goals and the advice of your healthcare provider. Generally, 20-30 minutes per session, 3-4 times a week, is effective for most purposes.
Can I Use Electrical Stimulation on Multiple Muscle Groups?
Yes, you can target multiple muscle groups, but focusing on one or two areas per session is advisable to avoid overstimulation.
Is Electrical Stimulation Safe?
Electrical stimulation is safe when used correctly. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult a healthcare provider with concerns.