Does Kidney Infection Cause Bloating? Understanding the Symptoms and Causes
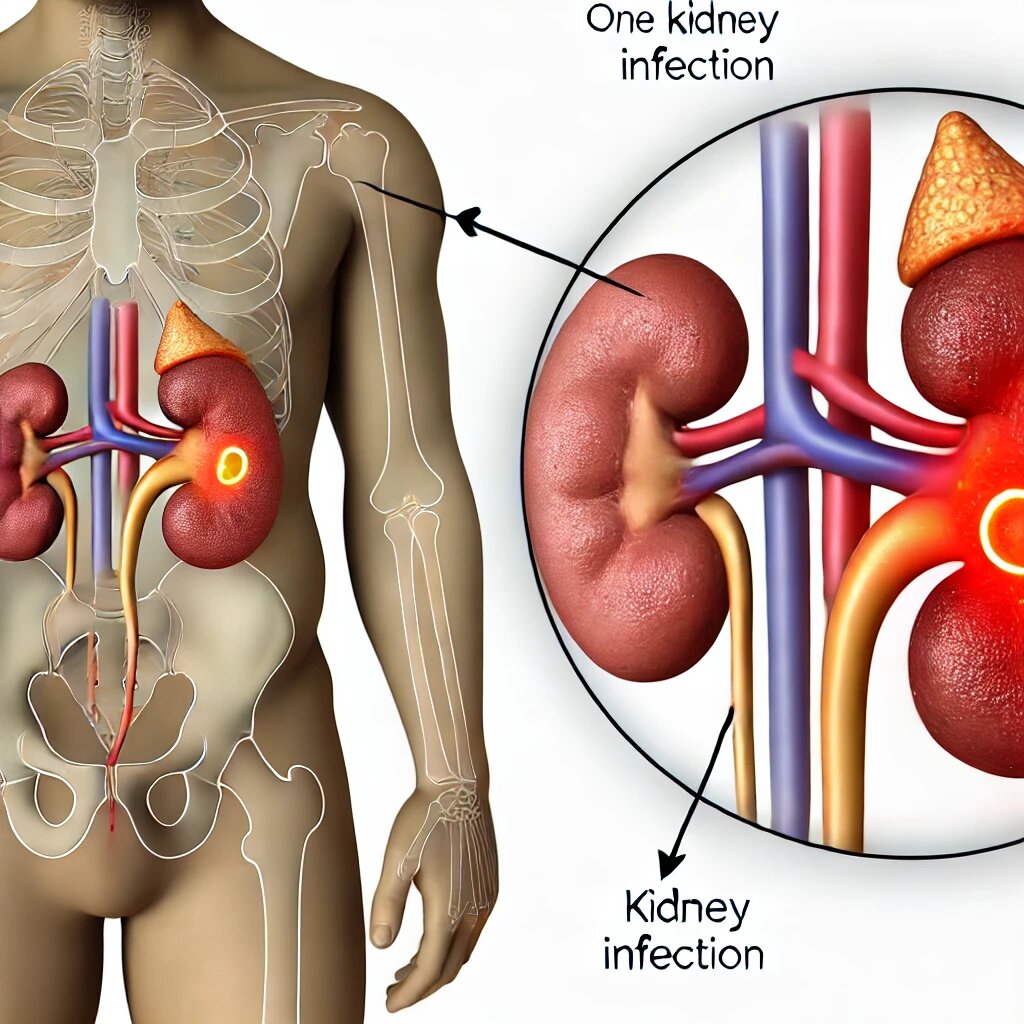
Kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that affects either one or both kidneys. It occurs when bacteria or viruses enter through the urinary tract through its urethra and migrate toward the kidneys via urinary drainage pathways.
While kidney infections are commonly associated with symptoms such as pain in the lower back or side and frequent urination, many people wonder if bloating can also be a sign of this condition.
What is a Kidney Infection?
A kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that originates in either the bladder or urethra and progresses up towards the kidneys. As severe medical conditions, they require prompt treatment to avoid complications. Common symptoms may include fever, back pain, frequent urination, and a burning sensation.
Kidney infections are typically caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract through urine passageways. Coli bacteria is one of the main culprits. At the same time, women are particularly prone to it due to shorter urethras, which make it easier for bacteria to access bladder and kidney tissues.
Understanding Bloating
Bloating, often associated with gas and abdominal discomfort, is an unpleasant sensation of fullness in the abdominal region that causes tightness or tightening, usually followed by swelling that makes your stomach visible larger than usual.
Bloating can be caused by numerous factors, including overeating, gas-producing foods, constipation, or hormonal shifts. It could also be a telltale sign of an underlying medical condition. Therefore, it’s essential to stay aware of any changes to your body and address them promptly.
Can Kidney Infection Cause Bloating?
Yes, a kidney infection can cause bloating. This is because a kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, often leads to inflammation and swelling of the kidneys and surrounding areas. This inflammation can cause abdominal discomfort and bloating.
symptoms of a kidney
- Pain in the back, side, or groin
- Frequent, urgent, or painful urination
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
Also Read: Kidney Stone Pain in Clitoris: Causes, Prevention, Treatment
The Link Between Kidney Infections and Bloating
The relationship between kidney infections and bloating underscores the interconnected nature of bodily systems. When the kidneys are infected, the subsequent cascade of bodily responses can indeed influence gastrointestinal health.
One of the primary mechanisms linking these conditions is inflammation. As the body combats the kidney infection, inflammatory cytokines are released, which can extend to other regions, including the digestive tract, culminating in bloating.
Treatment Options for Kidney Infections
Treating a kidney infection usually involves a course of antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection. The type and duration of antibiotic treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for intravenous antibiotics and fluids.
Pain management is also an essential aspect of treatment. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and reduce fever. It’s crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is fully eradicated and to prevent recurrence.
Indirect Causes of Bloating Due to Kidney Infections
Several factors related to kidney infections might indirectly lead to bloating:
- Antibiotic Use: Antibiotics are the primary treatment for kidney infections. While effective at eliminating the infection, antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut flora, leading to gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
- Dehydration: Kidney infections often result in nausea and vomiting, which can lead to dehydration. Dehydration slows down the digestive process, causing constipation and bloating.
- Abdominal Pain and Inflammation: The infection can cause significant abdominal discomfort and inflammation. This inflammation may extend to the gastrointestinal tract, leading to bloating and a feeling of fullness.
- Dietary Changes: During a kidney infection, patients may alter their diet to manage symptoms better. Sudden dietary changes, such as increasing fiber intake or consuming more fluids, can temporarily cause bloating as the body adjusts.
Managing Bloating from Kidney Infections
Managing bloating caused by kidney infections involves addressing both the infection and the underlying factors contributing to bloating. Taking prescribed antibiotics and staying hydrated are crucial steps. Additionally, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, and leafy greens into your diet can help reduce inflammation.
Avoiding gas-producing foods such as beans, carbonated drinks, and certain vegetables like broccoli and cabbage can also help alleviate bloating. Gentle exercise and abdominal massages can promote digestion and reduce the sensation of bloating.
When to Seek Medical Help
While mild bloating can often be managed at home, it’s essential to seek medical help if you experience severe or persistent symptoms. If bloating is accompanied by high fever, severe back pain, or difficulty urinating, it may indicate a serious kidney infection requiring immediate medical attention.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to preventing complications and ensuring a full recovery. Always consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your symptoms or if your condition worsens.
Conclusion
While bloating is not a direct symptom of kidney infections, it can occur due to various indirect factors associated with the condition and its treatment. Understanding the comprehensive symptoms of kidney infections and seeking timely medical intervention is crucial.
By managing the infection and supporting digestive health, the discomfort associated with bloating can be minimized. Prevention strategies play a vital role in reducing the risk of kidney infections and maintaining overall urinary tract health.
FAQ: Does Kidney Infection Cause Bloating?
How can antibiotics cause bloating during a kidney infection?
Antibiotics, used to treat kidney infections, can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
How does dehydration from a kidney infection lead to bloating?
Kidney infections can cause nausea and vomiting, leading to dehydration. Dehydration slows down digestion, which can result in constipation and bloating.
How is a kidney infection diagnosed?
A kidney infection is typically diagnosed through:
Urine tests: To detect bacteria, white blood cells, or blood in the urine.
Blood tests: To check for signs of infection and kidney function.
Imaging tests: Ultrasound or CT scans are used to visualize the kidneys and urinary tract.
What is the treatment for a kidney infection?
The primary treatment for a kidney infection is antibiotics. The specific type and duration depend on the severity of the infection. In severe cases, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics may be necessary.
When should I see a doctor if I suspect a kidney infection?
If you experience symptoms of a kidney infection, such as fever, chills, back pain, or painful urination, seek medical attention immediately. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications.