How Long until a Tooth Infection Kills You: Find Out Now!
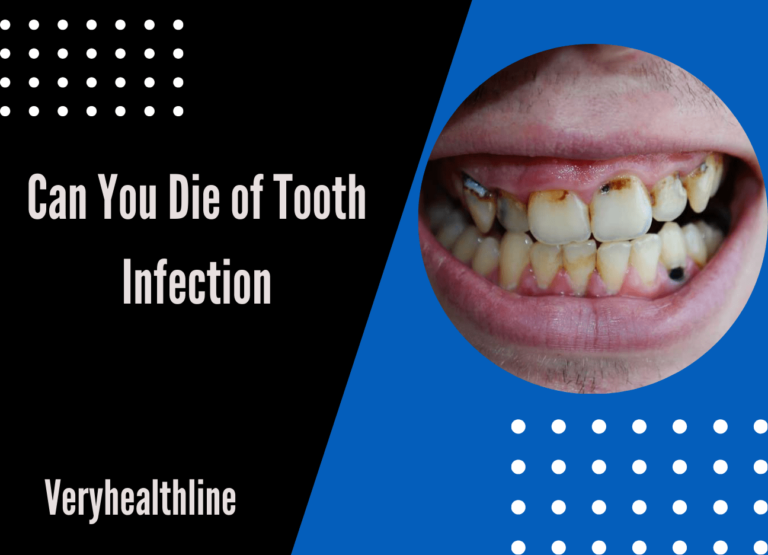
A tooth infection can be more than just painful and uncomfortable. If left untreated, it can lead to serious consequences. Many people are unaware of the risks associated with an untreated tooth infection, which could potentially be fatal if it spreads to other parts of the body. The common questions that arise about how a tooth infection can kill often center around the potential risks to teeth, bones, and long-term health.
If you ignore signs like tooth decay, cavities, or small abscesses, it could lead to a severe infection. Without a dental filling or quick, effective procedures, the infection can spread, causing distressing symptoms like throbbing tooth pain, fever, and increased tooth sensitivity.
Over time, the infection might affect the visible parts of your smile but can also travel deeper into the body, causing dangerous complications. Unfortunately, 50% of Americans don’t have dental coverage, which makes it harder to get the care they need and increases the risk of fatal infections. Seeking help from an emergency dentist is critical when you notice indicators of a serious tooth infection to avoid a race against time before the infection becomes fatal.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection, often referred to as a dental abscess, is a collection of pus that forms inside the tooth, gums, or even the bone that supports the teeth. This occurs when bacteria enter through a cavity or a crack in the tooth, leading to a bacterial infection.
As the infection worsens, a pocket of pus can form, known as a tooth abscess, which can spread from the surface of the tooth to the pulp, the innermost portion containing blood vessels and nerves.
The infection can result in severe swelling, inflammation, and an excruciating toothache, causing discomfort not only in the tooth but also in the surrounding gums and bone. Without proper dental intervention, complications can arise, including the spread of bacteria to the root and surrounding tissues, creating periapical abscesses at the tip of the tooth or periodontal abscesses in the gum area.
Causes of Tooth Infection
- Poor dental hygiene
- Deep cavities
- Trauma to the tooth
- Gum disease
- Cracked or chipped teeth
Signs and Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
The symptoms of a tooth infection can start off mild but escalate quickly if not treated. Common signs include:
- Severe toothache that doesn’t go away
- Swelling in the face or jaw
- Fever and chills
- Bad taste in the mouth or foul odor
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
If you notice any of these, especially swelling, it’s time to see a dentist right away.
Signs of an Infected Tooth
One of the most common signs of an infected tooth is throbbing pain that feels constant and often worsens when chewing. You may also notice swelling in the face, gums, or cheek, along with increased sensitivity to hot or cold food.
A tooth infection can lead to pus around the affected tooth and a bad mouth odor, which is hard to ignore. In severe cases, you might experience a fever, swollen lymph nodes, and even difficulty opening your mouth or trouble chewing.
Dentists classify dental infections into different types, such as periodontal, gingival, or periapical. A periodontal infection affects the gums and the supporting bone, while gingival disease impacts the gums directly. On the other hand, a periapical infection targets the tip of the tooth root, causing significant discomfort and requiring prompt treatment.
Also Read: What Does a Tooth Implant Look Like
Can a Tooth Abscess Kill You?
A tooth infection occurs when oral bacteria penetrate the core of the tooth, affecting the soft tissues and leading to a buildup of pus. This can happen due to tooth decay, chipped teeth, or damaged teeth. If left untreated, the infection can worsen and gradually spread to nearby teeth, tissues, and even the roots. As the infection progresses, it might lead to an abscess, which is essentially a pocket filled with pus that causes severe pain and potentially dangerous symptoms.
Although modern dentistry has advanced significantly and the chances of death from a tooth infection are rare in developed societies, it can still happen if the infection spreads to vital body parts.
In fact, in 1908, 10-40 percent of deaths were due to tooth infections, a shocking statistic for that time. Today, with the medical treatments available, this outcome is unlikely, but it’s essential to get infected teeth treated promptly to avoid severe complications.
How long before a tooth infection kills you?
The time frame for a tooth infection to become severe and life-threatening can vary widely. In some cases, the infection may progress overnight, while in others, it could take weeks or even months. An untreated infection can eventually spread throughout the body, leading to a fatal outcome.
The progression of the infection can move from mild to severe, and this is influenced by various factors like a person’s overall health. Those with compromised immune systems due to conditions like chemotherapy, HIV, or chronic diseases such as diabetes or kidney failure are more susceptible to the rapid progression of the infection.
As the infection spreads, the severity depends on how the individual’s body responds. Early treatment can halt the infection, while delayed treatment may require more aggressive intervention. Additionally, people with underlying medical conditions such as heart disease or lung disease face a worse prognosis if the infection spreads.
Older adults are at higher risk due to their reduced ability to fight infections. This increases the chance of morbidity and mortality from tooth infections, making prompt dental treatment essential for preventing serious complications and maintaining general well-being.
Can your body fight off a tooth infection?
A tooth infection should not be taken lightly. While the body can attempt to fight the infection, it often requires medical intervention. If left untreated, the bacteria causing the infection can spread and destroy surrounding tissue, leading to serious complications. It’s crucial to seek medical attention when you experience pain from a tooth infection.
Sometimes, the pain may subside as the pulp inside the tooth begins to die, but this does not mean the infection is gone. The bacteria can continue to spread, causing further damage. Only professional dental care can properly treat and prevent the infection from causing harm.
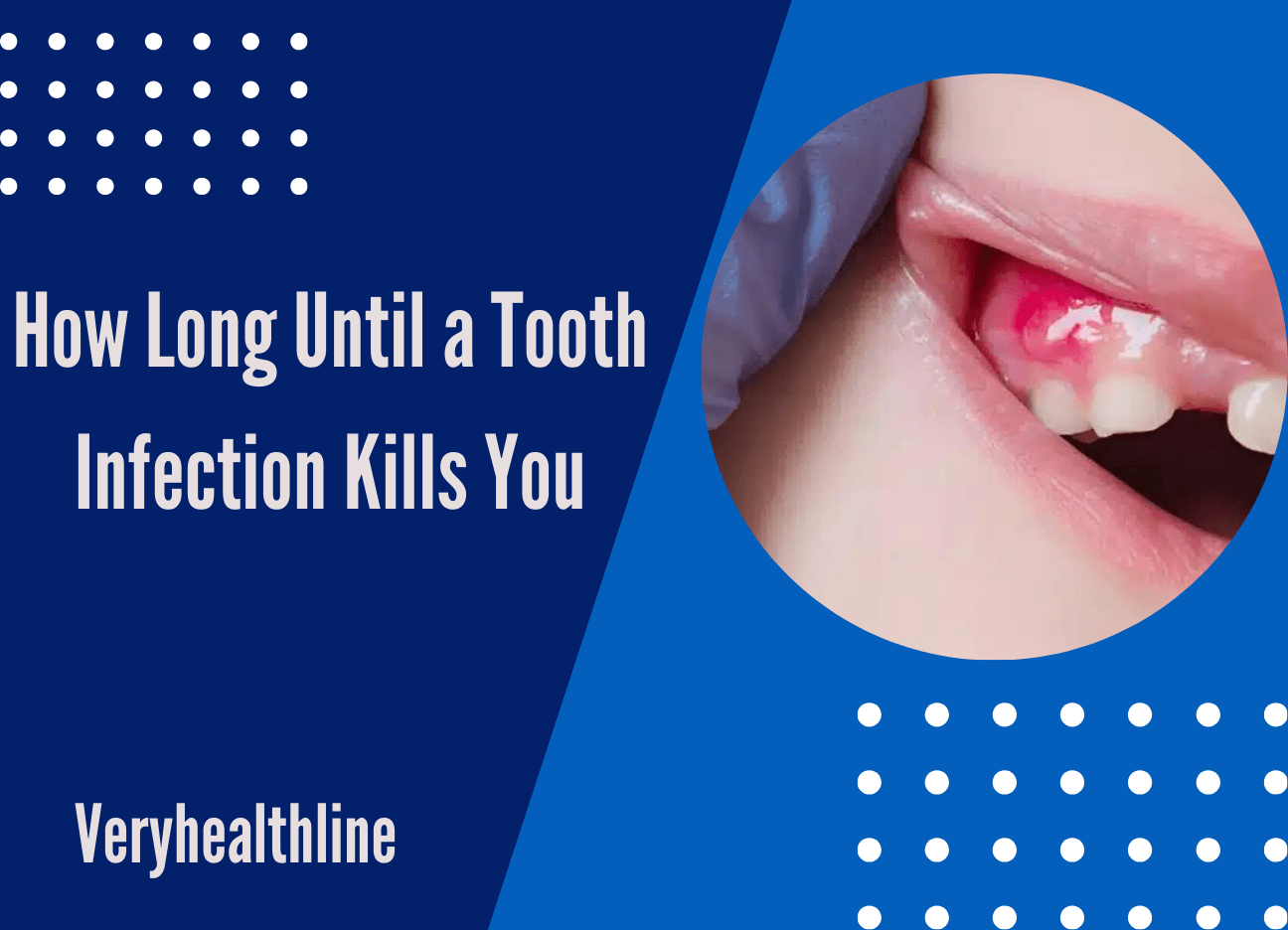
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You?
If you’re wondering how long it takes for a tooth infection to become serious, the timeline can vary. The infection usually develops from tooth decay or a tooth abscess, which can take several months to form.
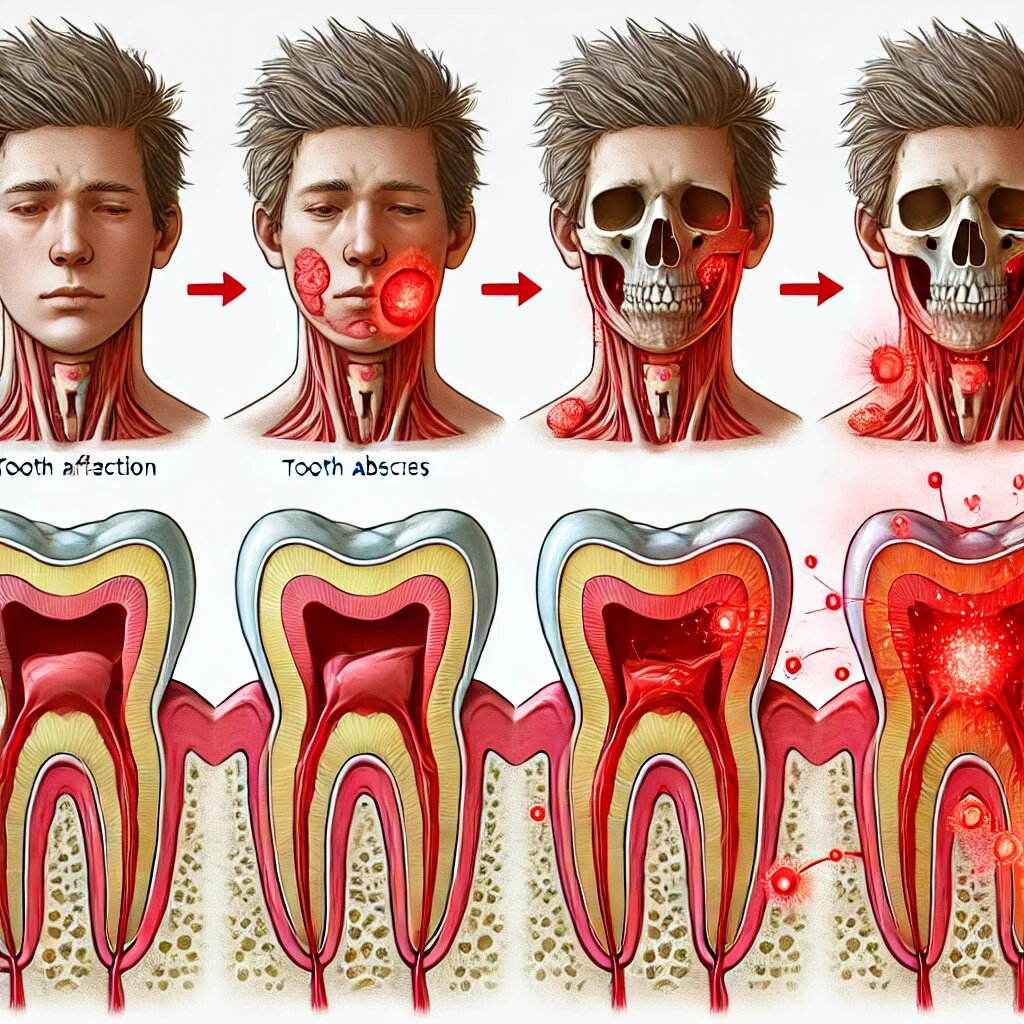
As the decay progresses, it can reach the pulp in the middle of the tooth, allowing bacteria to spread quickly, especially if there has been trauma or injury to the tooth. A serious tooth infection can develop faster in cases of injury, and common symptoms like a toothache, swelling, and an abscess around the affected tooth may appear.
If the infection is left untreated, it can spread through the body, even reaching critical areas like the brain, heart, or neck, and can cause death within a few days in extreme cases. Emergency dental care is necessary to stop the infection from spreading. With prompt medical treatment, including dental care, the risk of death can be significantly reduced.
How Do You Know If a Tooth Infection Has Spread to Your Blood?
When a tooth infection spreads to the blood, it can lead to sepsis, a severe condition that can become life-threatening. Though it’s rare, a bacterial infection from a tooth can result in serious complications if not treated early.
Sepsis occurs when the infection moves into the bloodstream and starts affecting major organs and body systems. Some signs that the infection has spread include a high fever, general soreness, and feeling unwell. If you notice these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Even though the risk of sepsis from a tooth infection is relatively low with proper care, the infection can become deadly if untreated. Early detection and treatment are key to stopping the infection before it causes severe damage.
Medical treatments can be administered quickly to help the body overcome the infection before it becomes life-threatening.
Risk Factors Associated with Tooth Infection
Certain patients are more prone to developing serious complications from a tooth infection. Key risk factors include having a weakened immune system, chronic health issues, and poor oral hygiene.
If left untreated, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, leading to life-threatening infections.
People with conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or those undergoing chemotherapy are at a higher risk of complications from a tooth infection. Early intervention is crucial to prevent the infection from spreading and causing more harm.
Older age
Older adults are at a higher risk of developing tooth infections that can lead to severe conditions. It is more common for elderly individuals to face severe medical complications from infections compared to other age groups.
Immunity
For immunocompromised patients or those with low immunity, the ability to fight infections is reduced. This means the body’s response is slower, and infections may take longer to heal, increasing the risk of complications.
Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing health complications from tooth infections due to impaired metabolism and a lack of insulin. This makes infections harder to manage and more dangerous.
Malnourishment
When your body is suffering from a dental infection, especially if it turns into a chronic condition, your immune system struggles. If you are malnourished, your body has a harder time fighting off infections. A weakened state increases the chances of complications.
How do I know if I have sepsis from a tooth infection?
When a tooth infection spreads, it can lead to sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition. In severe cases, your body’s immune system may start attacking its own tissues and organs. Though rare, a tooth infection can cause sepsis, and it’s essential to recognize the signs and symptoms early.
These include high fever, rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, low blood pressure, confusion, and extreme fatigue. If you’re ever concerned, seek medical help immediately, as sepsis can worsen quickly, causing chills and shivering.
FAQS:
Can a tooth infection go away on its own?
No, tooth infections do not heal on their own. Professional treatment is necessary to stop the infection.
How long can you have a tooth infection before it becomes fatal?
In severe cases, a tooth infection can become life-threatening within days to weeks, depending on your overall health.
What does sepsis from a tooth infection feel like?
Sepsis can cause fever, confusion, rapid breathing, and extreme weakness. It’s a medical emergency.
Can you die from an untreated abscess?
Yes, an untreated abscess can lead to severe infections like sepsis, which can be fatal.
Can a tooth infection affect your heart?
Yes, untreated infections can spread to the heart, causing endocarditis, a potentially fatal condition.